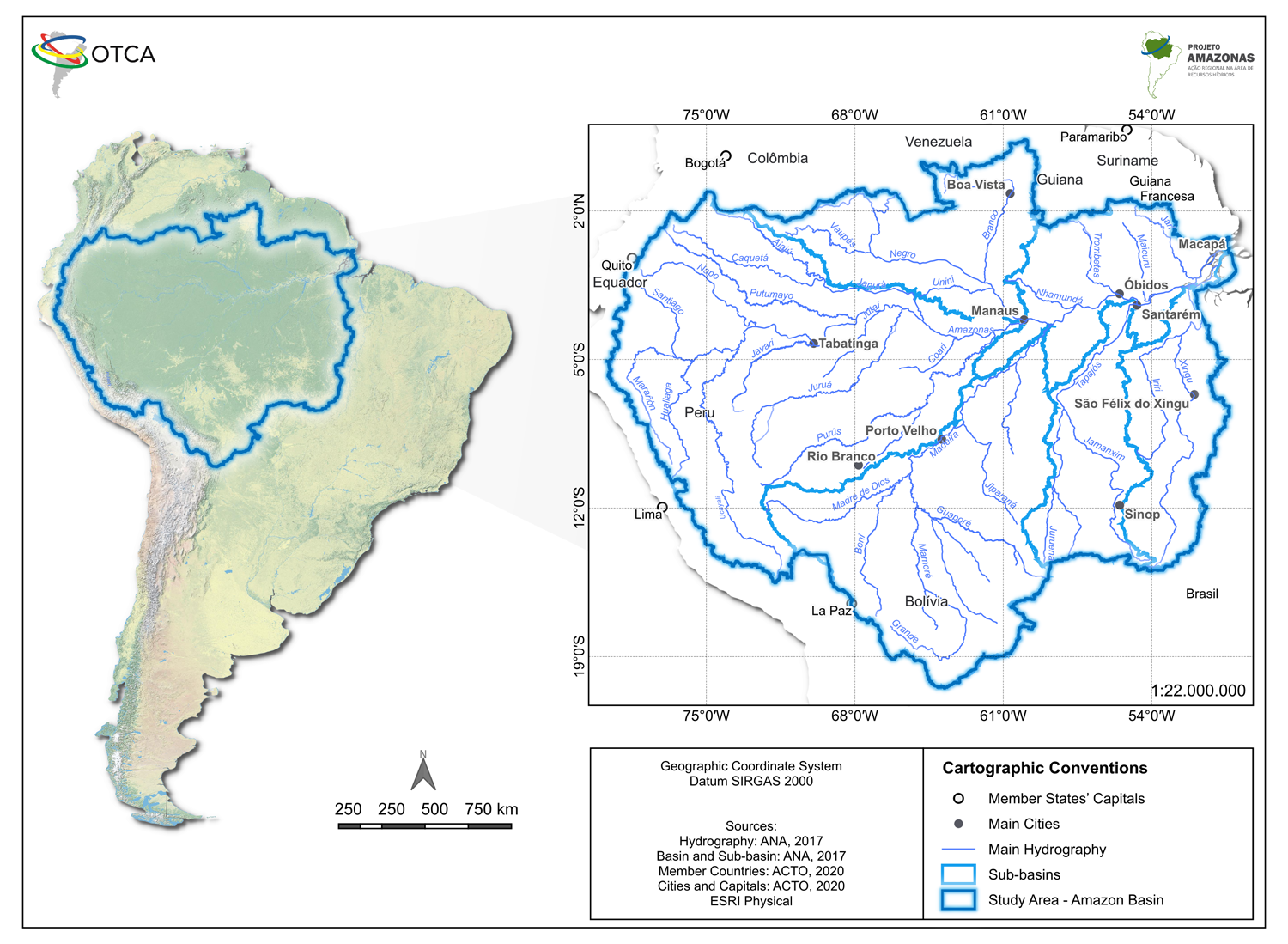
The Amazon Basin: a strategic global resource
The Amazon Basin covers approximately 5.9 million square kilometers, representing nearly 40% of the total territory of South America. This vast hydrographic system extends across eight countries and is home to more than 33 million inhabitants, making it one of the most strategically important regions for global environmental stability.
In addition to its impressive scale, the Amazon has incomparable strategic importance as the world’s largest freshwater reserve, containing approximately 20% of the planet’s available freshwater. Its river system generates crucial climate regulation services, sustains extraordinary biodiversity, and provides essential ecosystem services that extend far beyond regional borders.
* In the Amazonas Project, the delimitation of the Amazon Basin was established according to the Otto Pfafstetter method for the classification of hydrographic basins. For this reason, area and population data, among others, may be divergent from other ACTO projects that use another delimitation.
Integrated management and regional cooperation
The transboundary nature of the Amazon Basin requires unprecedented cooperation among the eight member countries of the Amazon Cooperation Treaty Organization (ACTO). Effective water resource management requires coordinated policies, shared monitoring systems, and unified conservation strategies.
Through integrated management approaches, countries can address common challenges, including climate change adaptation, sustainable development, biodiversity conservation, and equitable resource distribution, while respecting national sovereignty and indigenous rights.