The Amazon is crucial to maintaining global climate balance. It has a great influence on heat and water vapor transportation to higher latitude regions. It also has a particularly important role on atmospheric carbon sequestration, and consequently it contributes to the reduction of global warming.
All what is known about the Amazon is that it is huge, big, challenging and often immeasurable. The challenges of the past and future appear to impose in the present. It is essential to better understand its peculiarities and characteristics to act in benefit of the region.
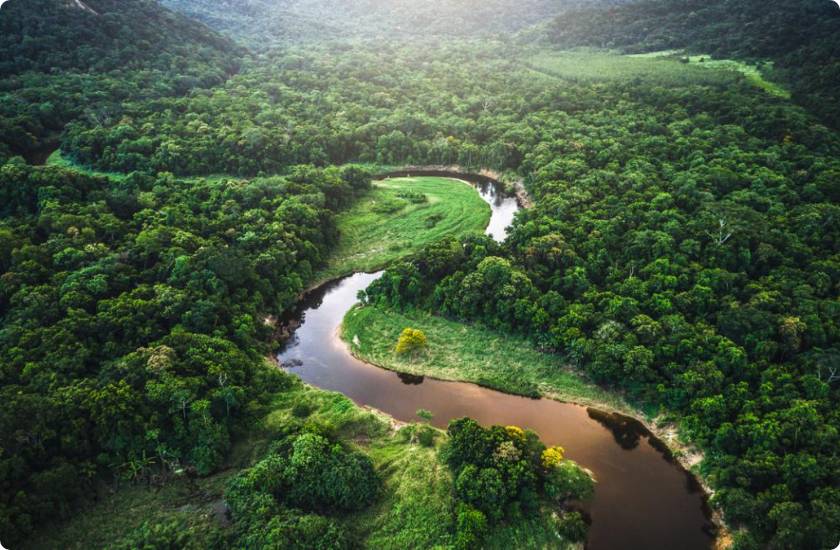
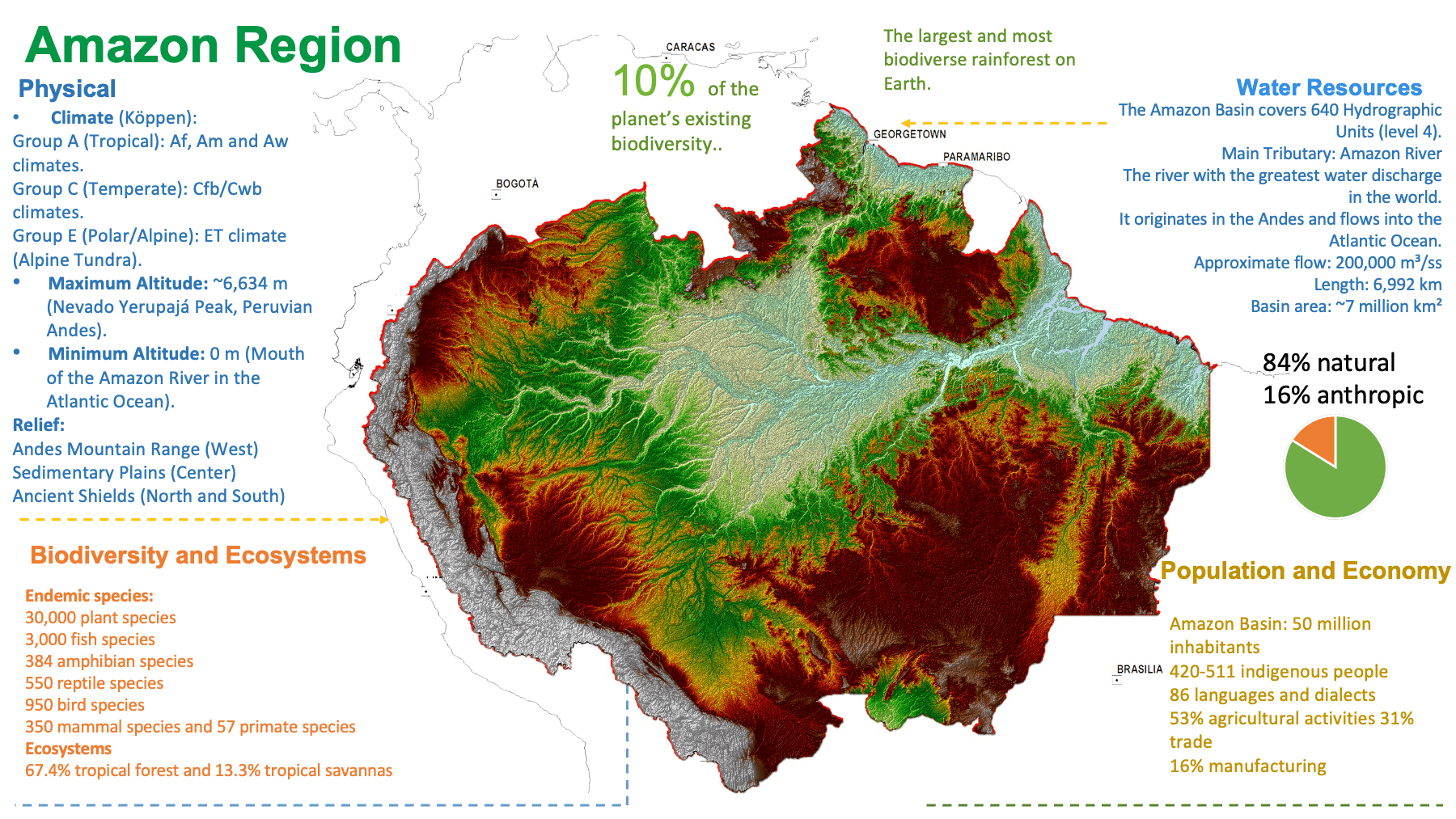
The Amazon is more than half of the world’s tropical rainforest and it is the world’s largest tropical forest. The region represents between 4 and 6% of the earth’s total surface and between 25 and 40% of the surface of America.
The Amazon is also a synonym of cultural diversity, which is the result of a historical process of land occupation and interaction among different ethnic and geographical origin groups.
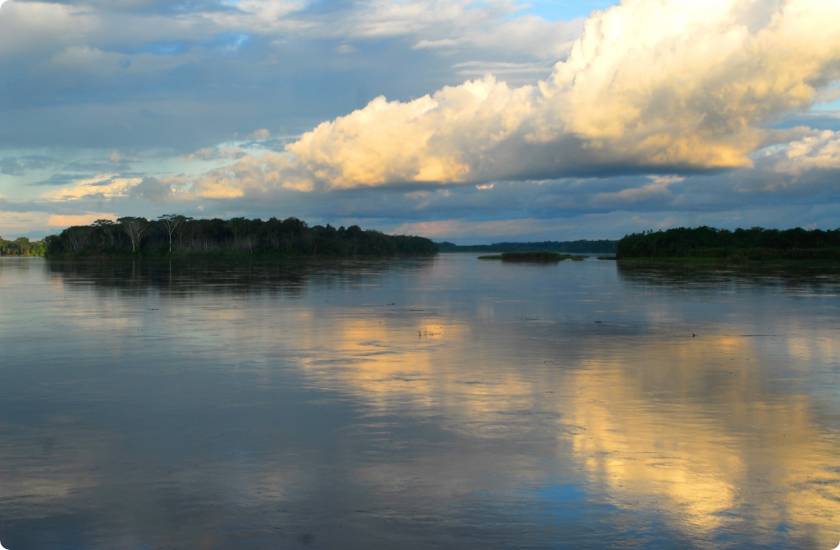
The Amazonian Hydrological Cycle feeds a complex system of aquifers and groundwater, which can cover nearly 4 million square kilometers among Brazil, Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and Venezuela.
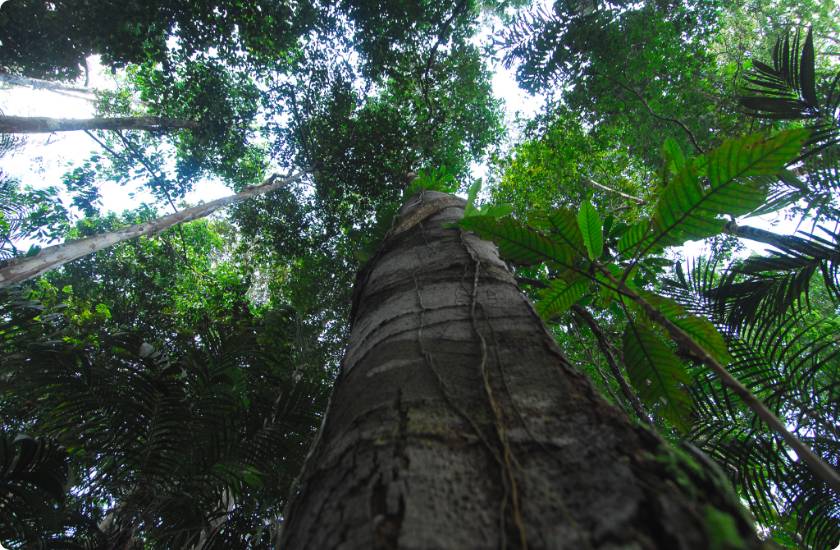
The Amazon is home to a variety of flora and fauna thereby allowing global brands of biodiversity to be set. It is also an important endemic area and is therefore a genetic reserve of global importance for the development of mankind.



